- May 13, 2025
- 3:57 am
The world is more connected than ever before. With the rise of e-commerce, digital payments, and streamlined logistics, exporting is no longer reserved for multinational corporations. Today, anyone From a small artisan to an ambitious entrepreneur, can tap into the $33 trillion global trade market.

Some Export Myths "You need a huge budget."
→ Many successful exporters started with less than $1,000.
"It’s too complicated."
→ With the right guidance, you can avoid common pitfalls.
"Only manufacturers can export."
→ Many exporters act as middlemen, sourcing products from local suppliers.
Exporting is the sale of goods or services from one country to another. It can be:
Direct Exporting – You sell directly to overseas buyers. This method allows businesses to establish direct relationships with foreign buyers, distributors, or retailers. This can lead to greater control over the sales process, including pricing, marketing, and distribution. However, it also requires more resources and expertise in navigating international trade regulations and cultural nuances.
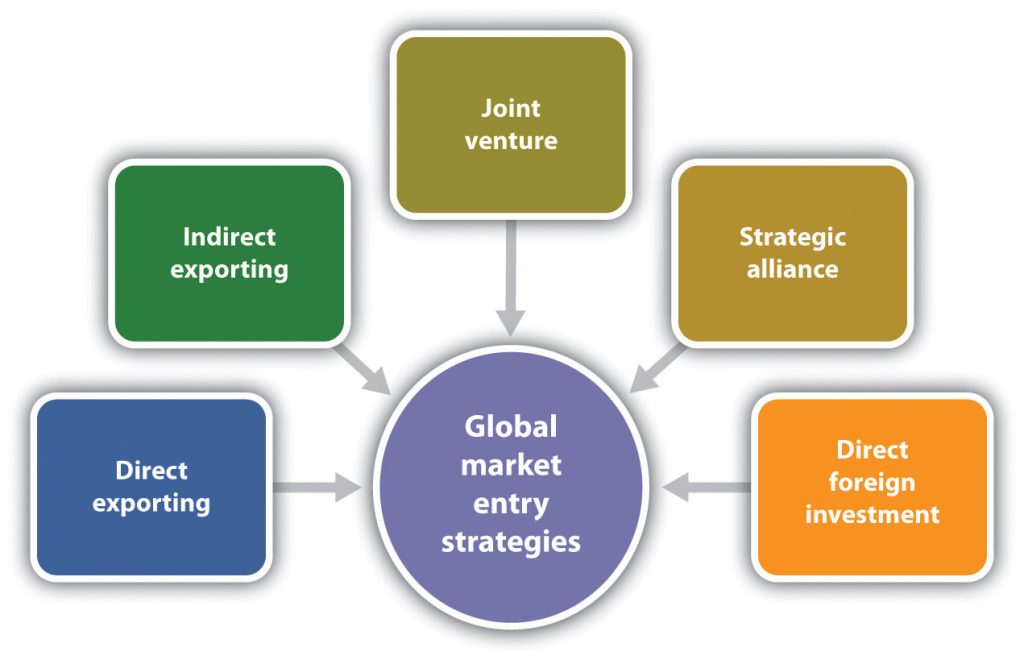
Indirect Exporting – You use intermediaries like agents or distributors. This can be a good option for businesses that are new to exporting or have limited resources. Intermediaries can provide valuable expertise and support, but they may also charge fees or commissions.
Dropshipping—Dropshipping is a retail fulfilment method where an online store sells products without holding any inventory. Instead, the store forwards customer orders and payment details to the manufacturer, wholesaler, or a third-party supplier, who then ships the product directly to the customer. This model allows businesses to avoid inventory costs and reduce operational overhead.
Some exporters fail due to a combination of factors, including improper and inadequate market research, inadequate knowledge of export regulations, errors in documentation, choosing the wrong supply lines, miscalculating costs, and failing to secure quality goods. Other contributing factors include lack of international experience, poor analysis of the export market, ignorance of government regulations and laws of the destination country, and weak financial strength. Additionally, supply chain disruptions, currency fluctuations, and a lack of understanding of basic international trade practices
can also lead to failure.
Letter of Credit (LC): Bank-issued guarantee that payment will be made to the exporter if terms are met.
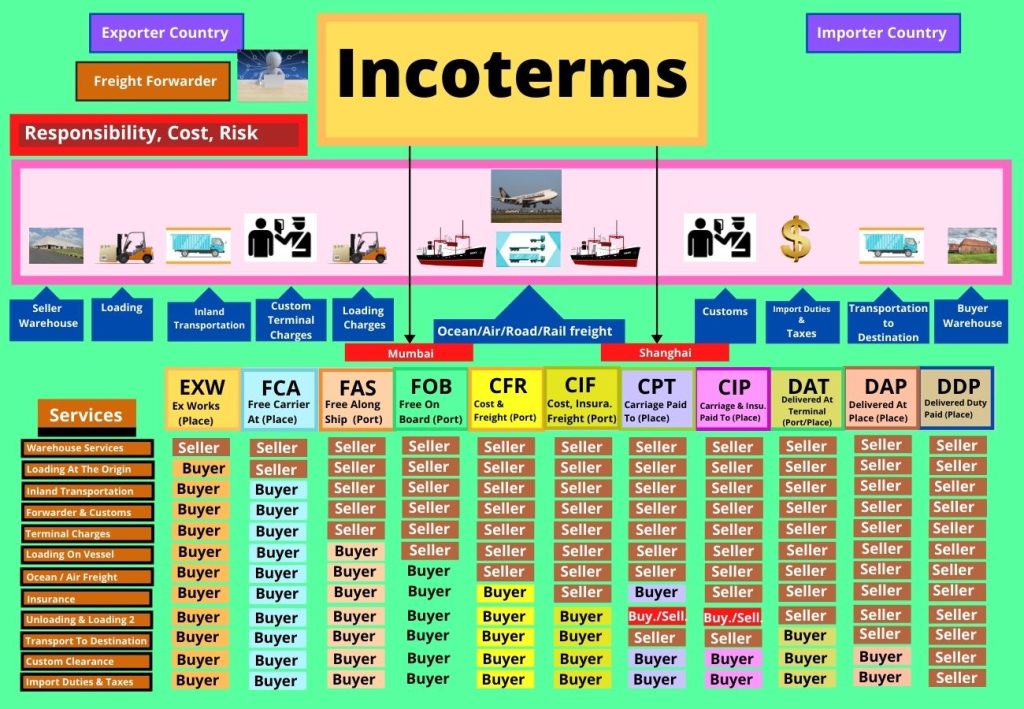
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These standardized trade terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers for delivery, insurance, and risk:
| Incoterm | Full Form | Key Responsibility Split |
| EXW | Ex Works | Buyer takes most responsibility |
| FOB | Free on Board | Seller delivers to port, buyer takes over at vessel |
| CIF | Cost, Insurance & Freight | Seller pays costs, insurance, freight to destination port |
| DAP | Delivered at Place | Seller delivers to named place, buyer handles import |
These are just some of the essential export terms. Familiarity with these concepts is vital for smooth international trade operations and compliance with global regulations
Key Steps to Find the Right Product for Export
1. Conduct Thorough Market Research
Use export data, trade reports, and market research tools to Identify global trends and products in high demand Investigate consumer preferences and cultural factors in potential target markets to ensure your product fits their needs.
2. Assess Product Uniqueness and Competitiveness
Select products that are distinctive, hard to replicate, or have a strong value statement. This helps you stand out from competitors, especially in markets dominated by low-cost suppliers. India’s strength lies in products-such as textiles, spices, handicrafts, and technology-where we have a competitive advantage.
3. Evaluate Profitability and Costs
First, calculate all costs involved: production, logistics, packing, shipping, taxes, insurance, tariffs, and compliance with international standards.
Then choose products with healthy profit margins and stable or growing demand. Low-volume, high-margin products (like jewellery or specialty handicrafts) can be more worthwhile for new exporters.
4. Ensure Supply Chain Reliability
Make sure you can source or produce the product regularly. Assess the availability of raw materials, suppliers, and backup options to avoid disruptions.
Products with a long shelf life (like metals and stones) reduce risk and inventory loss.
5. Study Trade Regulations and Market Entry Barriers
Check for export restrictions, import duties, and legal requirements in both your country and the target market.
Research trade relations between countries, as a favourable environment can open up opportunities or reduce costs.
6. Test Product Adaptability
Choose products that can be accepted or adapted to different market conditions. Products with wide usage and minimal modification requirements have a better chance of success.
7. Select the Right Target market
Checklist for Selecting Export Products
Is there a proven demand in international markets?
Can we offer a unique selling point or higher quality?
Are production and logistics costs sustainable and manageable?
Is the product still profitable after incurring all costs?
Are we compliant with all regulatory standards?
Is the product adaptable to diverse markets?
Do we have reliable suppliers and backup options?
Selecting the right product for export is a calculated process that requires in-depth research, market understanding, and careful financial planning. Focus on products that leverage your strengths, meet global demand, and offer sustainable profitability. Always stay updated on regulations and the latest market trends to maximize your export success.
Top 10 Beginner-Friendly Export Products
Top Portals for Export Product Ideas
| Portal/Platform | Main Focus | Key Benefits |
| Indian Trade Portal | Market research, policy, incentives | Tariffs, trade stats, e-bulletins, FAQs |
| IndiaMART | B2B marketplace | Wide product range, global buyer access |
| TradeIndia | B2B marketplace | Payment protection, loans, logistics |
| Exporters India | B2B marketplace | International reach for Indian manufacturers |
| Alibaba | Global B2B marketplaces | Access to global buyers, trend spotting |
| ExportHub | International B2B platform | Sourcing and global expansion |
| Pazago | Indian B2B portal | Advanced features for visibility and lead gen |
| Farmer Connect (APEDA | Agri-export sourcing | Connects exporters with farm product suppliers |
| FITA.org | Europages | Trade directories Lists of importers/exporters by region |
| NiryatBandhu | Training and mentoring | Export basics, product/market selection |
These portals collectively offer exporters a robust starting point for identifying promising product ideas, understanding market demand, and finding international buyers.
Best Platforms to Find Buyers Best Platforms to Find International Buyers
Expanding globally requires connecting with reliable international buyers. The most effective platforms for this purpose fall into two main categories: B2B marketplaces and ecommerce platforms with strong cross-border capabilities.
Top B2B Marketplaces for International Buyers
| Platform | Key Features & Focus | Global Reach |
| Alibaba.com | Largest B2B marketplace, all industries, bulk trade | Worldwide |
| Tradewheel.com | Fast-growing, broad categories, easy setup | Worldwide |
| Made-in-China | Focus on Chinese suppliers, global buyers | Worldwide |
| EC21 | Industrial focus, especially electronics/machinery | Worldwide |
| Volza | Streamlined exporter-buyer connections | Worldwide |
| ThomasNet | Industrial, strong in North America | Global |
| IndiaMART | Indian suppliers, international buyers | Global |
| EuroPages | European B2B, manufacturing, food, machinery | EU/Global |
| DHgate | Consumer goods, secure payment, buyer protection | Worldwide |
Mandatory Registrations and Documentations
Essential Export Documents
Procedural Steps
Other Considerations
Exporters must remain updated on amendments to export policies and regulations to avoid compliance issues and maximize available incentives.
Special provisions may apply for certain categories of goods, such as hazardous materials, defense items, or dual-use technologies, which are subject to international export controls and additional scrutiny.
By adhering to these legal and regulatory requirements, exporters can ensure smooth, lawful, and efficient international trade operations from India.
As per convenience we can choose any of the business models i.e
Finding trustworthy suppliers is the basic requirement of export business. Here's how to do it :
Here are some ways to find suppliers
1. Search for Local Manufacturers and Producers
2. Online B2B Marketplaces
3. Trade Fairs and Exhibitions
Key Considerations for Export Pricing:
Clearly define the responsibilities for shipping and other costs to avoid disputes and ensure accurate pricing.
Consider the impact of currency fluctuations and hedge against potential losses.
Factor in import duties, taxes, and other levies imposed by the importing country.
Adapt pricing strategies to the specific market conditions and customer preferences.

Effective packaging and labelling are crucial for international marketing to ensure product protection, facilitate customs clearance and to comply with local regulations.
Key considerations in export packaging:
Key considerations in export labelling:
Customs Broker: A customs broker is a licensed professional who acts as an intermediary between the exporter and the customs authorities to facilitate the movement of goods across international borders. They handle all the paperwork and formalities required for importing and exporting goods, ensuring compliance with customs laws and regulations.
Key responsibilities of a customs broker:
Customs brokers file all necessary documents, pay duties and taxes, and obtain required permits to ensure that goods clear customs smoothly.
They provide expert guidance on various laws regarding exports and imports, tariffs, and trade agreements, helping businessmen avoid penalties and delays.
By handling all the complexities of customs procedures, brokers allow businesses to focus on their core activities.
So, they are an important element in world trade.
Freight Forwarders:
They are intermediaries that organize the movement of goods from one place to another, working on behalf of shippers. They handle the logistics and paperwork associated with international shipping, ensuring goods are transported efficiently and legally.
Key responsibilities of a freight forwarder include:
1. Arranging Transportation
Choosing the most efficient and cost-effective mode of transport (sea, air, land) and coordinating with carriers.
2. Document Preparation
Completing the necessary shipping documents, customs forms, and other required paperwork
3. Customs clearance:
Facilitating the clearance of goods through customs at both origin and destination ports.
Freight Consolidation Combining smaller shipments into larger, to make economical loads for transport.
4. Warehousing and storage:
providing temporary storage and warehousing solutions as per need.
5. Cargo Insurance:
Arranging for adequate insurance coverage for protection of goods.
6. Liasing with other parties:
Working with carriers, custom brokers, and other parties involved to ensure smooth and efficient shipping.
Freight forwarders act as single point of contact for shippers , handling all aspects of international freight movement from start to finish.
Incoterms :
Secure Payment Options for Exporters
1. Advance Payment
2. Letter of Credit (L/C)
How it works: Bank guarantees payment upon document submission Types:
3. Documentary Collections
How it works: Banks handle documents against payment
Two types:
4. Open Account
5. Escrow Services
Currency hedging involves using financial instruments to mitigate the risk of losses due to fluctuations in currency exchange rates

Ways to hedge currency
Currency Hedging Strategies
To save ourselves from currency risks, it is better to
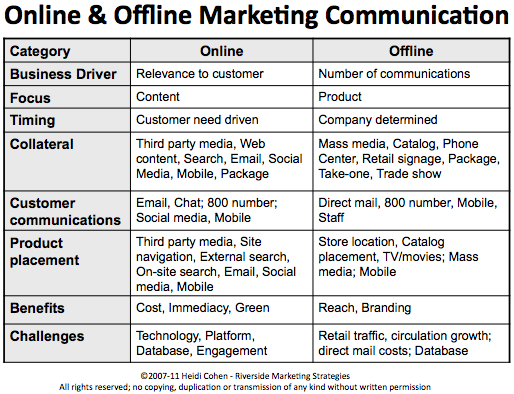
Online Marketing Strategies
Localized SEO:
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a crucial part of digital marketing for export, but it needs to be localized for each target market.
Targeted Content Creation:
Creating relevant and engaging content that resonates with your international audience is vital.
Social Media Engagement:
Leveraging social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn can help you connect with customers across borders.
Email Marketing:
Email campaigns are an effective way to communicate directly with potential and existing customers in international markets.
PPC Advertising:
Utilize Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising, like Google Ads, to drive traffic to your website from international markets.
Content Localization:
Adapt your website, brochures, and other marketing materials for each target market .
Market Research:
Thoroughly research your target markets to understand their needs, preferences, and online behavior.
Pricing Strategies:
Implement pricing strategies that are attractive and competitive in each target market.
Channel Selection:
Choose the right online marketing channels and platforms for your target market.
Digital Advertising:
Run targeted digital advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and Instagram Ads to reach your target audience .
Digital Marketing Plan:
Develop a comprehensive digital marketing plan that outlines your goals, strategies, and budget for international markets.
Monitor and Evaluate:
Continuously monitor and evaluate your digital marketing performance, using analytics tools to track key metrics and identify areas for improvement
Offline Marketing Tactics
Here's a more detailed look at some effective offline strategies:
1. Trade Shows and Exhibitions:
Networking:
Trade shows offer a valuable opportunity to meet potential customers, partners, and distributors face-to-face, fostering personal relationships.
Product Demonstrations:
Demonstrating products at trade shows can create a strong impression and showcase their value to potential buyers.
Printed Materials:
Distributing brochures, flyers, and other printed materials can reinforce brand messaging and provide informative resources.
Speaking Opportunities:
Being a featured speaker at a trade show can establish expertise and attract a captive audience.
2. Direct Mail Campaigns:
Targeted Messages:
Direct mail allows for customized messages and offers tailored to specific demographics and preferences in the target export market.
Postcards, Flyers, and Catalogs:
These physical materials can be used to announce new products, promote special offers, or provide information about your company.
3. Community Engagement:
Sponsoring Events:
Sponsoring local events or charities can build positive brand association and generate goodwill in the target market.
Participating in Community Initiatives:
Engaging with the local community can demonstrate a commitment to the target market and foster long-term relationships.
4. Press Releases:
Building Credibility:
Press releases can help establish your company's expertise and credibility in the target market by announcing major milestones or achievements.
Generating Media Coverage:
Press releases can be shared with local media outlets to gain coverage and build brand awareness.
5. Other Offline Tactics:
Offering Discounts and Samples:
Providing discounts or samples can incentivize potential customers to try your products and services, leading to conversions.
Building Business Networks:
Networking with industry professionals and potential partners in the target market can open doors to new opportunities.
Branded Merchandise:
Providing branded merchandise can create a memorable experience and reinforce brand recognition.
Flyers and Billboards:
These can be used to promote specific products or services or announce upcoming events
Building strong relationships with buyers in export business involves consistent communication, providing high-quality products, and demonstrating reliability. It's also crucial to understand the buyer's needs and preferences, offering competitive pricing, and providing excellent customer service.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Regular Contact:
Maintain regular communication with buyers, providing updates on orders, shipping timelines, and any relevant information.
Prompt Responses:
Respond promptly to inquiries and address any concerns or questions in a professional manner.
Follow-up:
Follow up after initial contact to gauge interest and ensure the buyer's needs are being met.
High-Quality Products:
Prioritize quality and ensure your products meet or exceed the buyer's expectations.
Reliable Shipping:
Partner with reliable logistics providers to ensure timely and safe delivery of goods.
Warranty and Support:
Provide clear warranty information and offer adequate support to address any issues that may arise.
Understanding the Buyer:
Feedback: Actively seek feedback from buyers to identify areas for improvement.
Build Trust:
Be honest and reliable in all dealings, building a reputation for trustworthiness.
Some common export challenges faced by exporters are:
1.Customs Delays Solution:
Hire an experienced customs broker Prepare all documents in advance
2.Payment Defaults Solution:
Use L/C or trade insurance Credit check new buyers
3.Quality Disputes Solution:
Establish a strong quality control system Conduct pre-shipment inspections.Clear product specifications in the export contract
4.Shipping Damage
5.Currency Fluctuations
Solution: Hedge currency risks trade in stable currencies
6.Language Barriers
7.Regulatory Changes
8.Supplier Issues
9.Market Entry Barriers
10.Logistics Complexity
Solution: Work with experienced freight forwarders
Utilize technology solutions like advance tracking systems and blockchain for real time data sharing.
11.Crisis Management
Scaling an export business involves expanding operations beyond the current scope, typically by increasing production, expanding into new markets, or improving efficiency. This can be achieved through various strategies like identifying new markets, building stronger buyer relationships, optimizing logistics, and leveraging government incentives.
Here's a more detailed look at how to scale an export business:
1. Market Research and Expansion:
Identify new markets:
Conduct thorough research to identify countries or regions with high demand for your products or services.
2. Building Strong Relationships:
Provide excellent customer service and build strong relationships with buyers, as repeat business and positive word-of-mouth are crucial for long-term success.
3. Explore partnerships:
Consider partnering with international distributors or agents to help expand your reach and access local markets.
4. Optimizing Operations:
Streamline logistics:
Optimize your supply chain and logistics processes to ensure efficient and timely delivery of goods.
5.Leverage technology:
Utilize online platforms, digital marketing tools, and other technologies to improve efficiency and reach more customers.
6.Secure financing:
Explore various financing options to support your expansion, such as loans, lines of credit, or grants from government programs.
7.Monitor cash flow:
Closely track your cash flow and manage your finances effectively to ensure you can meet your obligations and invest in growth.
8. Utilizing Government Schemes and Incentives:
Investigate government schemes and incentives designed to support exporters, such as tax breaks, subsidies, or trade facilitation programs.
9.Seek expert advice:
Consult with trade advisors or export consultants to learn about available opportunities and navigate complex regulations.
10.Monitor market trends:
Keep abreast of changes in market trends, consumer preferences, and emerging technologies to stay ahead of the competition.
Several individuals from diverse backgrounds have successfully transitioned from ordinary roles to become exporters, demonstrating that export business is accessible to anyone with the right drive and knowledge. For example, Shree Hari Kaliya, an engineer with an IT background, transitioned into exporting pulses after a family-suggested import-export course. Similarly, Devang Shah, through e-commerce, resells unclaimed imported goods auctioned by customs, targeting international markets.
Here's a closer look at some success stories:
Import Export Business Success Story of Shree Hari Kaliya
1. Shree Hari Kaliya: This young engineer, encouraged by his father, took an online import-export course and identified pulses, a family-related product already sold domestically, as a potential export item.
2. Devang Shah: He leverages e-commerce to purchase and resell unclaimed imported goods, focusing on international markets and utilizing e-commerce platforms for efficient transactions and pricing advantages.
3. Jack in the Box Toys: This Mumbai-based toy brand expanded its business globally through e-commerce, becoming a top export brand from India.
4. Priyank Gupta (Firozabad): He saw an opportunity to export glass and glassware, turning around a period of business slackness and experiencing a positive trend in overseas shipments.
These stories highlight the versatility of the export market and how individuals can leverage their existing knowledge, resources, or even find new opportunities through online platforms and courses.
Now we have enough of knowledge. Knowledge will not work unless we take steps to start export business. So ,take immediate action and start an adventurous journey of export business.
Feature Post
Popular Post
Browse Category
Subscribe News Letter
This design is incredible! You most certainly know how to keep a reader amused.
Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start
my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic job. I really loved what you
had to say, and more than that, how you presented
it. Too cool!
Also visit my webpage … space insta bio
Thank you sir for sharing your ideas. i will be happy if you guide me to keep a reader amused.